Drinking water is essential for life, and encouraging employees to stay hydrated in the workplace is key to supporting both their long-term health and organizational productivity. But, with so many types of water available — from purified water, spring water, and sparkling water to distilled water and mineral water — it can be challenging to determine which option is best to provide at work.
For teams in pursuit of a clean water supply that can promote health and performance, we’re taking a closer look at the difference between purified water and distilled water — so you can find the option that’s best suited for your workplace.
What’s the Difference Between Purified Water and Distilled Water?
Purified Water
Purified water, typically made with groundwater or tap water, goes through a filtration process to remove various impurities and contaminants. Some of the most common impurities that are filtered out include:
- A broad spectrum of harmful chemicals
- Algae
- Bacteria
- Parasites
- Fungi
- Traces of certain metals like lead and copper
When it comes to the purification system used to clean water, there’s a wide range of techniques used today, both commercially and in homes. But first, let’s take a look at why tap water often needs a purification boost.
Public drinking water goes through standard water filtration, comprised of the following treatment methods:
- Coagulation: Positively charged chemicals are added to the water supply to neutralize the negative charge of dirt and other dissolved particles.
- Flocculation: The water source is mixed to form larger, heavier particles called flocs.
- Sedimentation: Flocs settle to the bottom, separating solids from the water.
- Filtration: The clean water that was isolated by sedimentation and left on the top is filtered again to separate additional solids from the water.
- Disinfection: One or more chemical disinfectants, such as chlorine or chlorine dioxide, can be added to the filtered water to kill any remaining contaminants or bacteria.
However, while the standards for public drinking water are set by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), it’s important to note that water quality differs everywhere, which impacts the filtration process and the resulting cleanliness. This means tap water, although monitored and filtered, is not generally as clean as it could be. That’s where additional techniques for purification come into play.
Purification Techniques
Some of the most common methods to effectively remove impurities and contaminants from drinking water include:
- Deionization: In this water purification system, two types of ions are removed to create deionized water: positively charged “cations” and negatively charged “anions.” Cations include minerals like calcium, magnesium, iron, and sodium, while anions comprise chloride, sulfates, nitrates, carbonates, and silica.
- Boiling water: Simply boiling water is a valid way to kill disease-causing germs, including viruses, bacteria, and parasites, as reported by the CDC. This is generally considered an efficient water purification method when you don’t have access to safe, treated water.
- Reverse osmosis (RO): To make reverse osmosis water, harmful contaminants and other impurities are removed by using pressure to force water molecules through a semipermeable membrane. Once these chemicals and contaminants are filtered out, you’re left with clean, pure water.
Methods of water purification can vary, but at the end of the day, they’re aiming to produce the same results — pure water. And, according to Sensorex, for water to be considered “purified,” it must have lower than 10 ppm (99% of all contaminants should be removed).
Distilled Water
Distilled water, on the other hand, is a type of purified water that goes through the distillation process to remove impurities and other water contaminants. Distillation essentially works by boiling water and collecting the steam, which eventually returns to a liquid state once cooled.
Purdue University reports that this water purification system is highly effective at removing impurities like:
- A wide range of bacteria and viruses.
- Protozoa like giardia.
- Harmful chemicals such as sulfate and lead.
Distilled water is often used in laboratories and facilities due to the resulting water purity. It’s not as common to drink water that’s been distilled, but because it’s free of impurities it’s unquestionably safe to do so. However, it’s important to note that this powerful purification process inevitably removes essential minerals. That means no chemicals or impurities, but no taste or good stuff either.
The Advantages and Potential Drawbacks of Each Water Supply
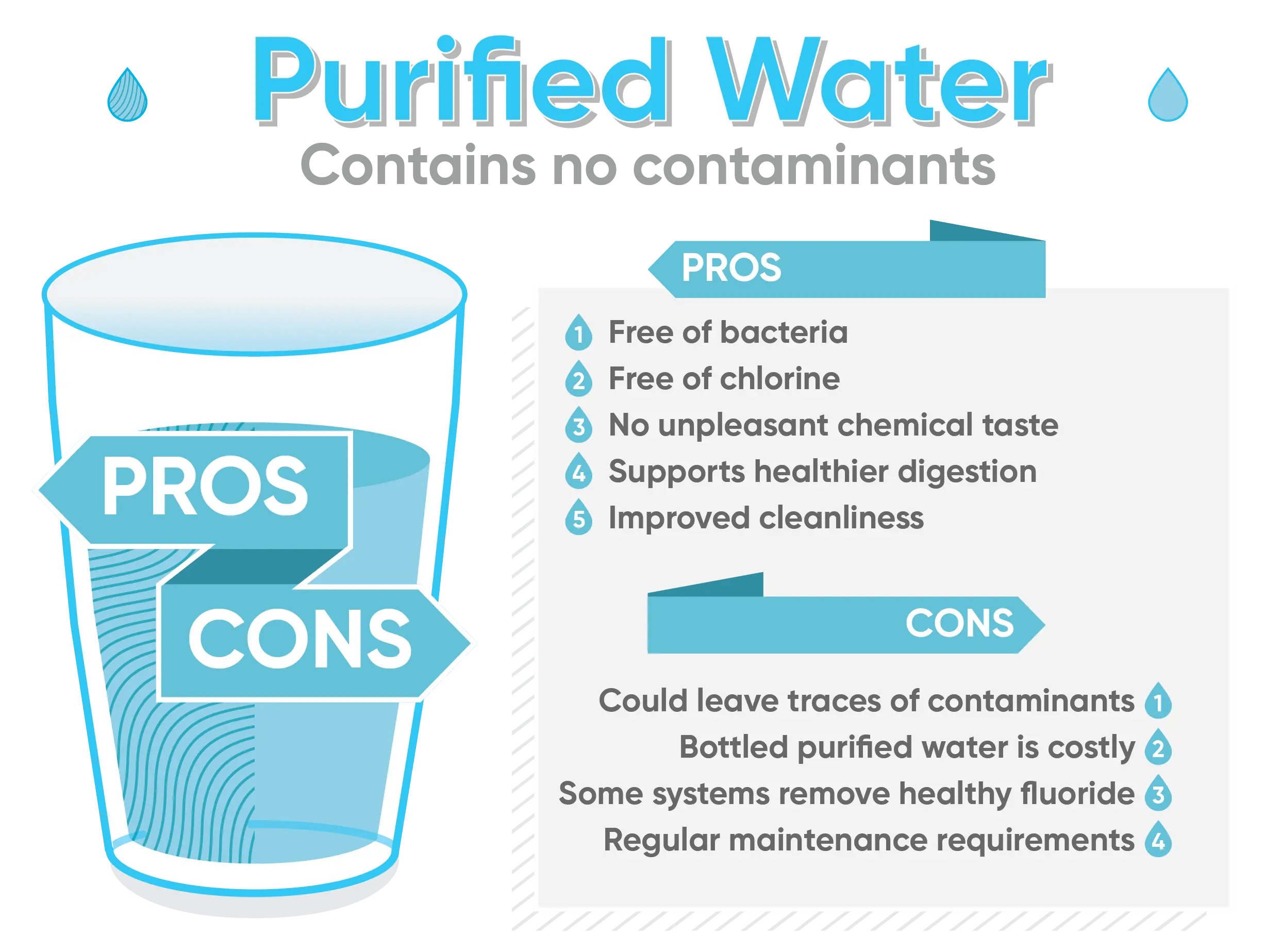
The Pros and Cons of Purified Water
The EPA sets legal limits for over 90 harmful contaminants in tap water to ensure it’s considered safe for consumers to drink. However, an effective purification system can take this filtration process to the next level for an even cleaner result. Various purification methods ultimately promote several valuable benefits:
- Purification successfully removes bacteria that can lead to adverse health effects (e.g., nausea and stomach aches).
- Systems for purification like charcoal filters remove chlorine, a common chemical added to the public water supply as a disinfectant and linked to a higher risk of certain cancers.
- Filtration removes unpleasant tastes associated with organic matter, chemical treatments, or metal plumbing.
- Drinking purified water supports a healthier colon and digestive tract.
- Most purification systems improve the cleanliness of tap water, especially in areas with lower water quality.
Although purified water has clear advantages, it’s equally essential to consider what you need to be cautious of when drinking this type of water:
- Some purification processes aren’t as effective at removing contaminants as distillation. As a result, it’s possible for impurities to be left behind, including chemicals and pesticides.
- Opting for bottled water to gain access to pure water is costly and unsustainable.
- Certain purification systems remove the fluoride in tap water, which is known to reduce tooth decay and support overall dental health.
- Some filtration and purification systems require maintenance and upkeep to ensure the water filter maintains effectiveness over time.
The Pros and Cons of Distilled Water
Despite the fact that distilled water and purified water are closely related, aiming to produce clean water results, water that’s been distilled has unique advantages and disadvantages to take into account. Consider the following benefits:
- Distillation is a particularly impressive technique to remove contaminants from water.
- Because of a lack of impurities like bacteria and pesticides, distilled water is beneficial for individuals with weakened immune systems (e.g., people with HIV/AIDs or cancers).
- Drinking water that’s been distilled can support the health of individuals who live in areas with low-quality water and filtration standards.
- Distilling water effectively removes chlorine from the water, which boosts its taste.
However, this impressively clean water isn’t without its downsides:
- Similar to most purified water, the distillation process also removes fluoride, which means individuals who drink distilled water will need to pay extra attention to their dental health.
- While being free from contaminants, this type of water also lacks electrolytes and natural, healthy minerals — like magnesium and calcium — which are important for your health.
Which Option Is Best?
So, with everything in mind, what’s the best option to drink? Well, the truth is there’s no one right answer. As long as you’re drinking water that’s being filtered and treated properly — so you can rest assured it’s safe to drink — then the type of water you choose is entirely dependent on personal preference.
Both distilled water and purified water are cleaner than tap water and support your overall health. The main difference between these water types is that distilled water will always remove the minerals and electrolytes and not all purification processes will have the same result: In particular, reverse osmosis filtration will also remove any minerals present, whereas boiling and deionization will not.
Fortunately, workplaces can consider a water filtration system that gives them the best of both worlds. We’ll take a closer look at how Quench is helping organizations do this below.
Provide Purified Water With a Bottleless Water Cooler at Work
When businesses and workplaces are in search of water that’s just as clean as distilled water but has the essential minerals needed to support the long-term health of their workforces, Quench can help. Quench offers water-as-a-service solutions by providing filtered water through a broad array of bottleless machines to help organizations keep their employees, customers, and guests happy, healthy, and hydrated.
Some of our most popular bottleless dispensers provide quenchWATER+, our Quench-branded mineral-infused and electrolyte-enhanced alkaline water. This cutting-edge technology takes on-demand water to the next level through a 5-filter setup:
- Sediment filter
- Pre-carbon filter
- RO filtration
- Mineral + filter
- Polishing filter
This process is designed to remove sediments, contaminants, and bad tastes while adding minerals and electrolytes back — ensuring the cleanest result that includes the healthy minerals your employees need. And this cooler connects directly to your building’s existing water line, so your teams and customers have access to an endless supply of fresh, filtered water as needed.
With a bottleless water cooler from Quench, you can provide clean, great-tasting water that supports the health of your valuable team members, regardless of your area’s local water quality. Try our product finder to discover the machine your business needs or get a free quote to get started.